Blog
“Understanding the Different Types of TPMS: Direct vs. Indirect Systems”
Understanding the Different Types of TPMS: Direct vs. Indirect Systems
The Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) is an essential safety feature that alerts drivers when tire pressure drops below the recommended levels. However, not all TPMS systems are created equal. There are two primary types of TPMS: Direct TPMS and Indirect TPMS, each with unique technology and benefits. Understanding the differences can help you make an informed decision about your vehicle’s needs.
Why Is TPMS Important?
Proper tire pressure is critical for:
- Safety: Reducing the risk of blowouts or poor handling.
- Fuel Efficiency: Preventing increased fuel consumption caused by underinflated tires.
- Tire Longevity: Avoiding uneven wear and extending the life of your tires.
TPMS ensures you’re promptly alerted to any pressure issues, but the type of system determines how this information is collected and reported.
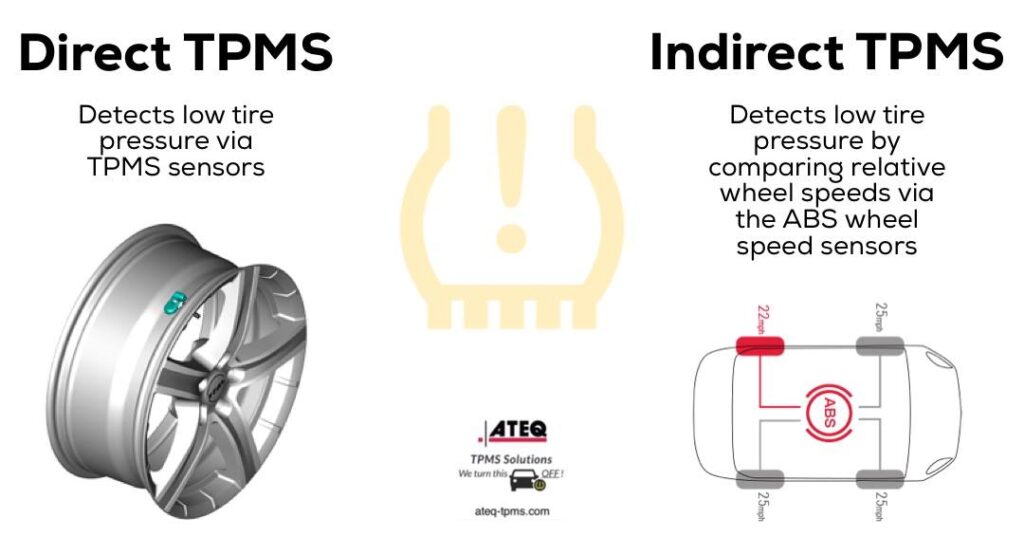
Direct TPMS: Precision at Its Best
Direct TPMS is the more advanced of the two systems, using dedicated pressure sensors inside each tire.
How It Works
- Sensors measure the air pressure in real time.
- The data is transmitted wirelessly to the vehicle’s onboard computer.
- If the pressure drops below a pre-set threshold, a warning light or message appears on the dashboard.
Advantages of Direct TPMS
- Accuracy: Delivers precise pressure readings for each tire.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Provides instant alerts for pressure changes.
- Tire-Specific Alerts: Pinpoints which tire has an issue, saving time during inspection.
Drawbacks of Direct TPMS
- Higher Cost: Sensors are more expensive to manufacture and replace.
- Battery Maintenance: Sensor batteries typically need replacement every 5-10 years.
- Potential Compatibility Issues: Custom wheels may require adjustments or specialized sensors.
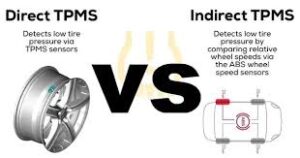
Indirect TPMS: Simplicity and Cost-Effectiveness
Indirect TPMS doesn’t measure tire pressure directly but instead uses the vehicle’s Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) sensors to estimate it.
How It Works
- The system monitors wheel speed and rotation patterns.
- Underinflated tires have a smaller diameter, causing them to rotate faster.
- Discrepancies in rotation rates trigger a warning on the dashboard.
Advantages of Indirect TPMS
- Cost-Effective: Less expensive to manufacture and maintain.
- No Battery Dependency: Operates without the need for in-tire sensors.
- Easy Maintenance: Doesn’t require regular battery replacements or recalibration for new tires.
Drawbacks of Indirect TPMS
- Less Accurate: Can’t measure exact tire pressure or identify which tire is underinflated.
- Calibration Required: Needs recalibration after tire rotations, replacements, or pressure adjustments.
- Limited Alerts: May not detect gradual pressure loss or minor underinflation.
Comparing Direct and Indirect TPMS
| Feature | Direct TPMS | Indirect TPMS |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Highly accurate, real-time readings | Estimates pressure indirectly |
| Tire-Specific Alerts | Identifies the exact tire | Does not specify affected tire |
| Cost | Higher initial and maintenance cost | More affordable |
| Battery Requirement | Requires battery replacements | No battery needed |
| Calibration | Minimal recalibration required | Requires frequent recalibration |
| Compatibility | May need adjustments for custom wheels | Works with standard ABS systems |
Which TPMS Is Right for You?
The choice between Direct and Indirect TPMS depends on your priorities and vehicle needs:
- Choose Direct TPMS if:
- You want precise pressure readings for each tire.
- Accuracy and real-time alerts are critical to your driving habits.
- You don’t mind the higher upfront and maintenance costs.
- Choose Indirect TPMS if:
- You’re looking for a budget-friendly solution.
- Your vehicle already has an ABS system compatible with indirect monitoring.
- You don’t require highly detailed pressure data.
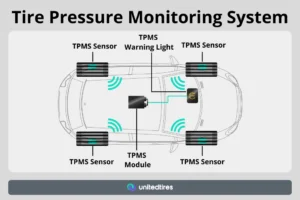
Aftermarket TPMS Options
If your car doesn’t come equipped with a TPMS, you can opt for an aftermarket system. Many aftermarket TPMS options offer features like:
- Smartphone connectivity for real-time monitoring.
- Compatibility with both Direct and Indirect systems.
- Custom alerts tailored to your preferences.
The Future of TPMS
As automotive technology evolves, we’re seeing innovations that blend the accuracy of Direct TPMS with the affordability of Indirect TPMS. Emerging systems include:
- Integrated Vehicle Health Monitors: Combining TPMS with other safety features like brake monitoring.
- Smartphone Integration: Allowing drivers to monitor tire pressure remotely.
- Eco-Friendly Sensors: Focused on reducing environmental impact during manufacturing and disposal.
Final Thoughts
Both Direct and Indirect TPMS have their strengths and weaknesses, and the right choice depends on your budget and needs. Whether you prefer the precision of Direct TPMS or the cost-effectiveness of Indirect TPMS, these systems are essential for maintaining tire safety, improving fuel efficiency, and reducing long-term vehicle costs.
For more insights into vehicle safety and performance, visit RegalXmuse.com—your ultimate resource for automotive expertise.